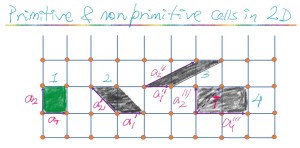
Primitive and non-primitive cells in 2-D. All pair of vectors of each cell shown are translation vectors of the given lattice. But vectors of cell 4 are not primitive translation vectors. Hence cell 4 is not primitive cell. Its because lattice translation vector T can’t be formed by any integral combination of the corresponding pair of vectors. But for all other cells the pair of vectors are primitive translation vectors. Cell 1, 2 and 3 each are primitive cells and they are all equal in area. Cell 4 has twice the area of the other 3 cells.
Primitive and non-primitive cells in 2-D. All pair of vectors of each cell shown are translation vectors of the given lattice. But vectors of cell 4 are not primitive translation vectors. Hence cell 4 is not primitive cell. Its because lattice translation vector T can’t be formed by any integral combination of the corresponding pair of vectors. But for all other cells the pair of vectors are primitive translation vectors. Cell 1, 2 and 3 each are primitive cells and they are all equal in area. Cell 4 has twice the area of the other 3 cells.
Posted
in
by
Tags:
Leave a comment