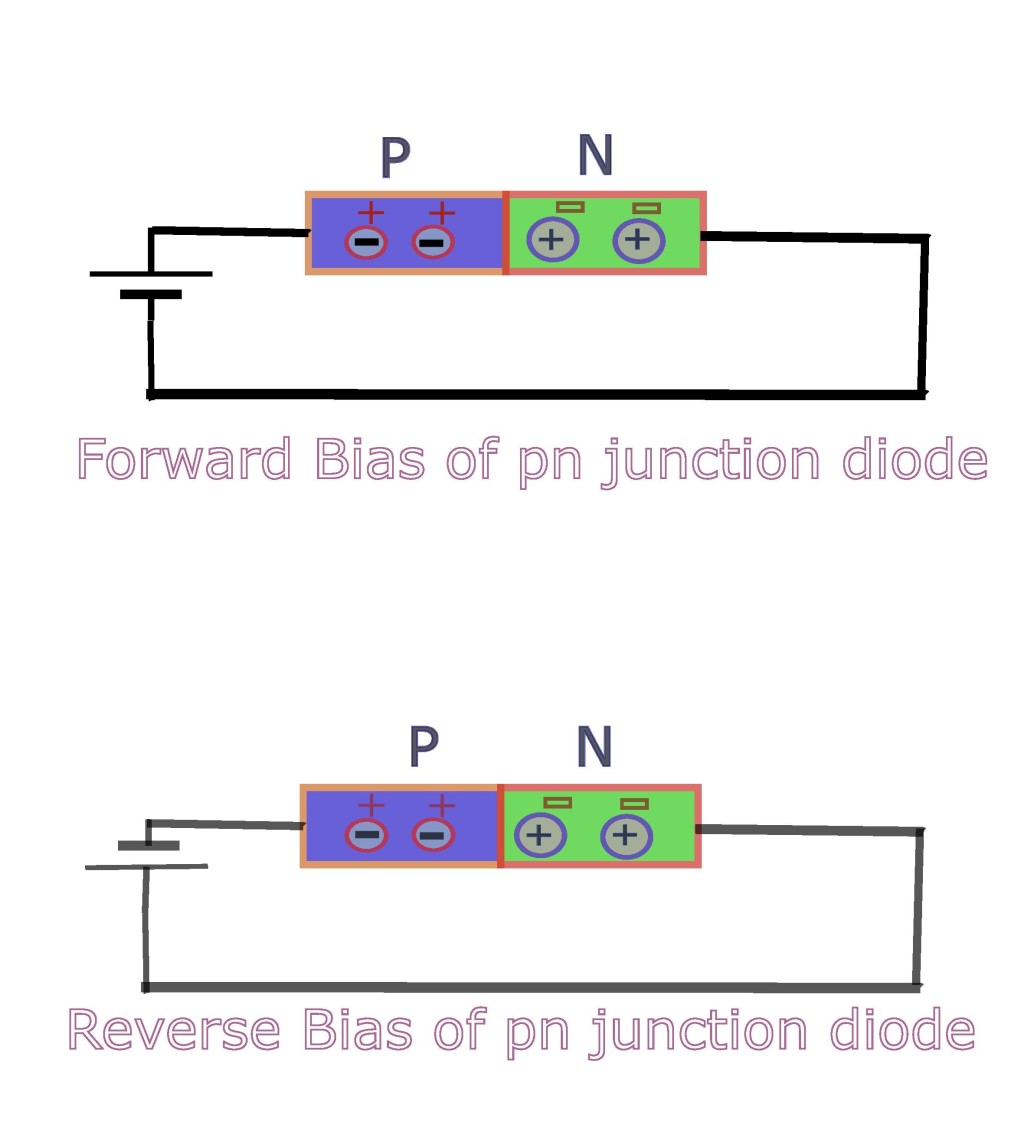
Category: Teaching
-
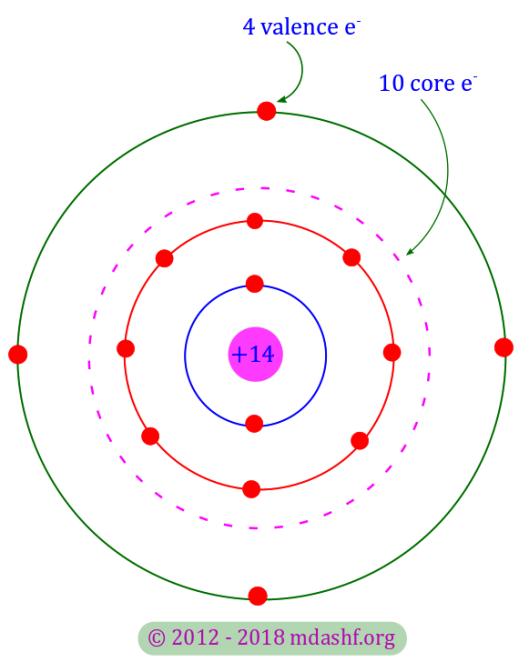
Conductivity and mobility in semiconductors, L-III
We will discuss in this lecture about drift velocity of electrons and holes in semiconductors which leads to the conductivity and mobility of free charge carriers in the same. To smooth-sail through this lecture you might wanna first brush up the concepts discussed in the last two lectures: lecture I and lecture II. Lets begin…
-
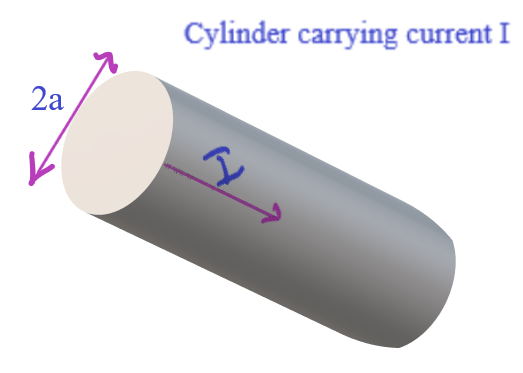
Problem 5.13 Application of Ampere’s Law.
Yesterday we saw an interesting application of the Ampere’s Law (– in magnetostatics and sometimes called Ampere’s circuital law also) for the infinite uniform surface current. Today we will see yet another display of the elegance and efficacy of this law in the following problem. This problem is inherited from Griffith’s text on Electrodynamics (3rd…
-
Maxwell Boltzmann distribution for a classical ideal gas
i. We assume a dilute gas which is enclosed by a thermally insulated container on all sides. Dilute gas in a thermally insulated container: Dilute means concentration of gas molecules is low. Insulated implies there is no reasonable flow of heat energy across the walls of the container. ii. Each molecule is assumed to be a…
-

If you would like to become a nuclear physicist, what you would like to know about the nucleus first?
A. structure of the nucleus Every atom consists of a dense positive central core of mass, known as nucleus. Its size is much smaller compared to the size of the atom, nut nonetheless it contains almost all of the mass of the atom. The nucleus is made of only neutrons and protons. — These are…