Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
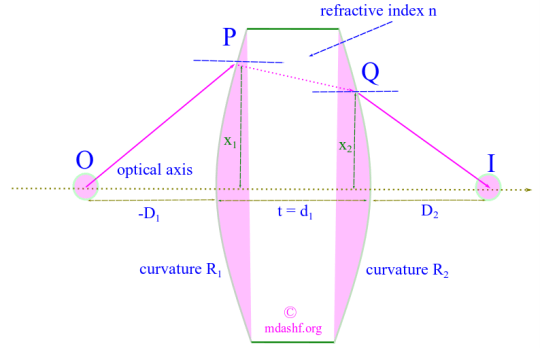
Application of matrix method to thick lens
Optics Series Lecture, Lecture — VI All Optics series articles: https://mdashf.org/category/optics/. Application of Matrix Method to Thick Lenses Topics covered in this lecture A. Cardinal points B. Thick lens equation and matrix for thick lens C. System matrix for thin lens D. Unit and Nodal planes E. Matrix for a system of 2 thin lenses Our previous studies of…
-
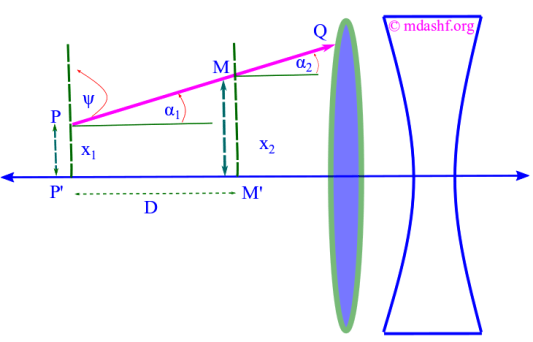
Matrix formulation in geometrical optics
Topics covered in this lecture Ray tracing a. Translation matrix b. Refraction matrix c. System matrix In this lecture, we will discuss about one of the most interesting and powerful methods in Geometrical Optics. As we have discussed here (https://mdashf.org/2017/02/25/fermats-principle-a-lecture-in-optics/), geometrical optics is that segment of optics in which we are limited to a situation…
-
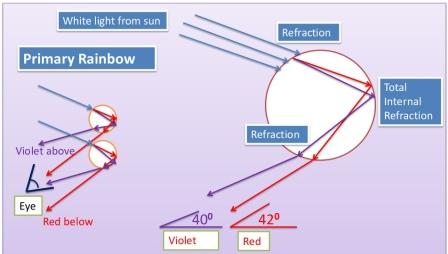
How rainbows are created
How Rainbows are created. Optics lecture series – IV “Primary and Secondary rainbows”, a lecture in Optics. This lecture was delivered on February 02, 2017. Sunlight is white in color. Do you know Newton would have greatly disliked this statement, do you know why? “Color is not the property of light” but a property of an…
-

Fermat’s Principle, a lecture in optics
Optics series lecture, Lecture-III “Geometrical Optics and Fermat’s Principle”. Geometric Optics: When the size of objects that a wave of light interacts with are large compared to the wavelength of light λ, λ can be neglected for practical purposes and the light waves behave like rays of light. Rays of light are geometric line segments…
-

Primary aberration, a lecture in optics.
Lecture-II; delivered on 27-1-2017 In our Lecture-I we discussed the phenomena of aberrations that arise because of a discrepancy of a first order theory and the 3rd order theory as depicted by the Maclaurin series; where we saw that first order theory represents the so called paraxial optical systems. Please have a look of the linked…
Got any book recommendations?