Category: basic physics
-
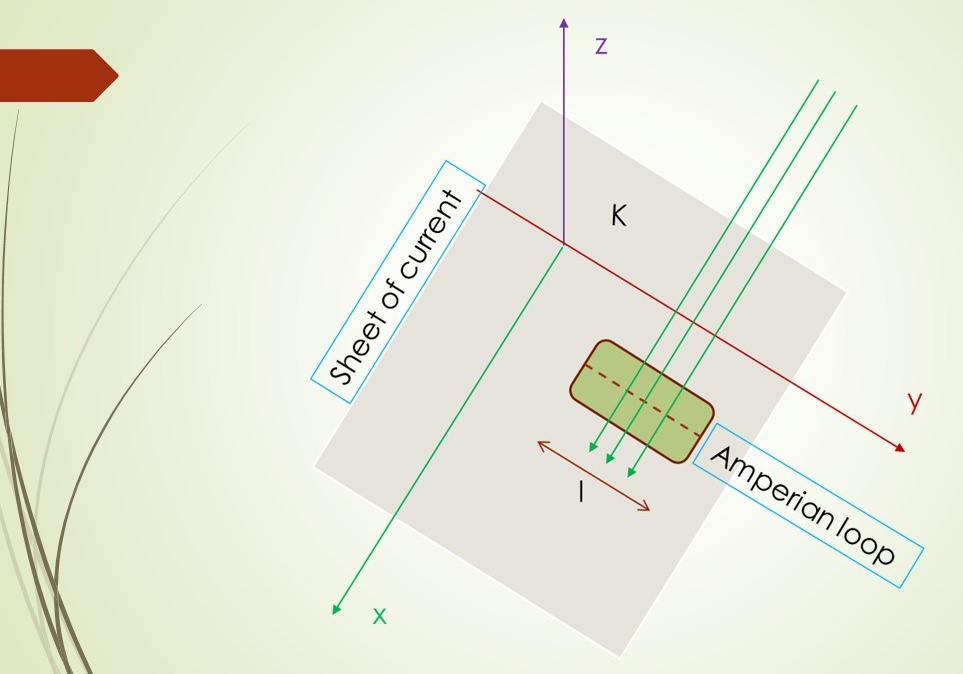
Example 5.7; Application of Ampere’s law.
The following problem is an interesting application of Ampere’s law apart from usual applications found in honors syllabus (eg infinite straight conductor, Solenoid and Torroid). This is to be found the excellent book by Griffith on Electrodynamics. Find the magnetic field of an infinite uniform surface current K (vect) = K i-cap, flowing over the…
-
Maxwell Boltzmann distribution for a classical ideal gas
i. We assume a dilute gas which is enclosed by a thermally insulated container on all sides. Dilute gas in a thermally insulated container: Dilute means concentration of gas molecules is low. Insulated implies there is no reasonable flow of heat energy across the walls of the container. ii. Each molecule is assumed to be a…
-

Helmholtz theorem in electrodynamics, Gauge transformation.
Electromagnetic theory, lecture — IV Topics covered in this lecture a. Helmholtz theorem — in electrodynamics b. Gauge transformation — of scalar and vector potential in electrodynamics c. Coulomb and Lorentz gauge All electromagnetic theory lectures of this series, will be found here (https://mdashf.org/category/electromagnetic-theory/) In our previous lecture — lecture — III, we discussed in quite detail,…
-

Helmholtz theorem. Scalar and vector potentials
This lecture develops the formalism of electrodynamics in a very methodical way. It covers the following topics in detail. A. Formalism of electrodynamics — fundamental theorem B. Application of Helmholtz theorem — to electrostatics C. Application of Helmholtz theorem — to magnetostatics
-
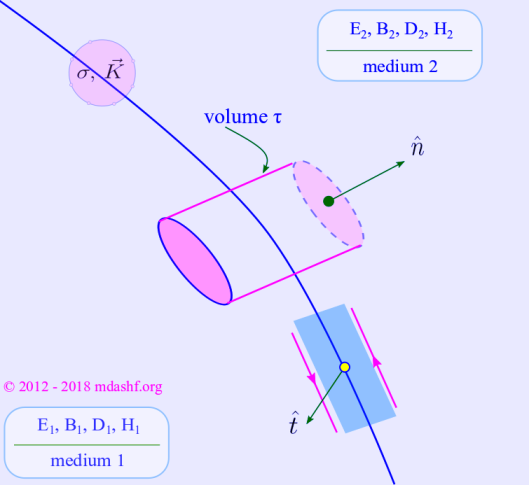
Boundary conditions on electric and magnetic fields.
Electromagnetic theory, Lecture — II. Boundary conditions on Electric and magnetic fields in Maxwell’s equations Topics covered A. Summary of Maxwell’s equations — in free space and in material media B. Integral forms of Maxwell’s equations — by application of vector calculus C. Derivation of boundary conditions — on electric and magnetic fields In the last…