Author: Invariance, MDASHF i@M
-
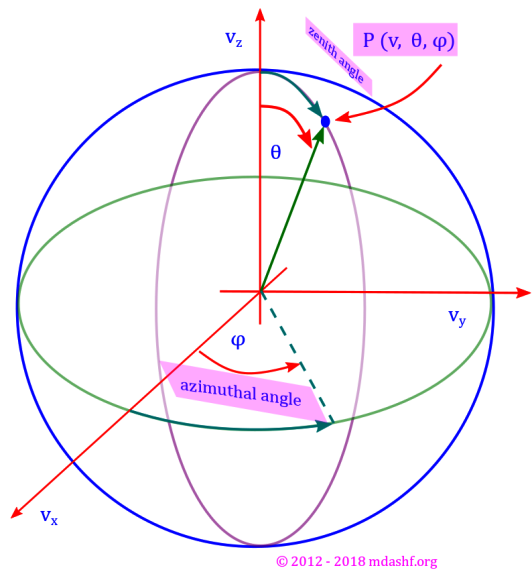
Conservative Nature of the Electrostatic Field and Electrostatic Potential, Lecture – 4.
Today we will discuss the conservative nature of the static electric field — the time varying fields are not amenable to this conservative nature as we would learn in an advance discourse. This is intimately connected with the concept of the Helmholtz theorem which has been discussed on this website (linked below), in an advance…
-
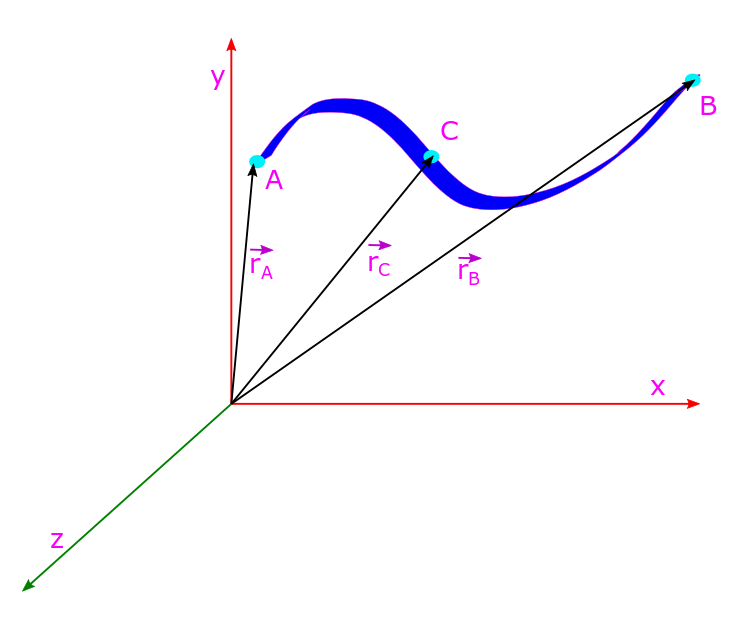
Application of Gauss Law, Spherical Symmetry, Lecture-3
In our last two lectures we laid a good foundation about the concepts of electric field, lines of force, flux and Gauss Law. They can be found here; EML1 and EML2. In the last one we discussed how to apply Gauss Law to find the electric field if cylindrical or planar symmetries are present in…
-

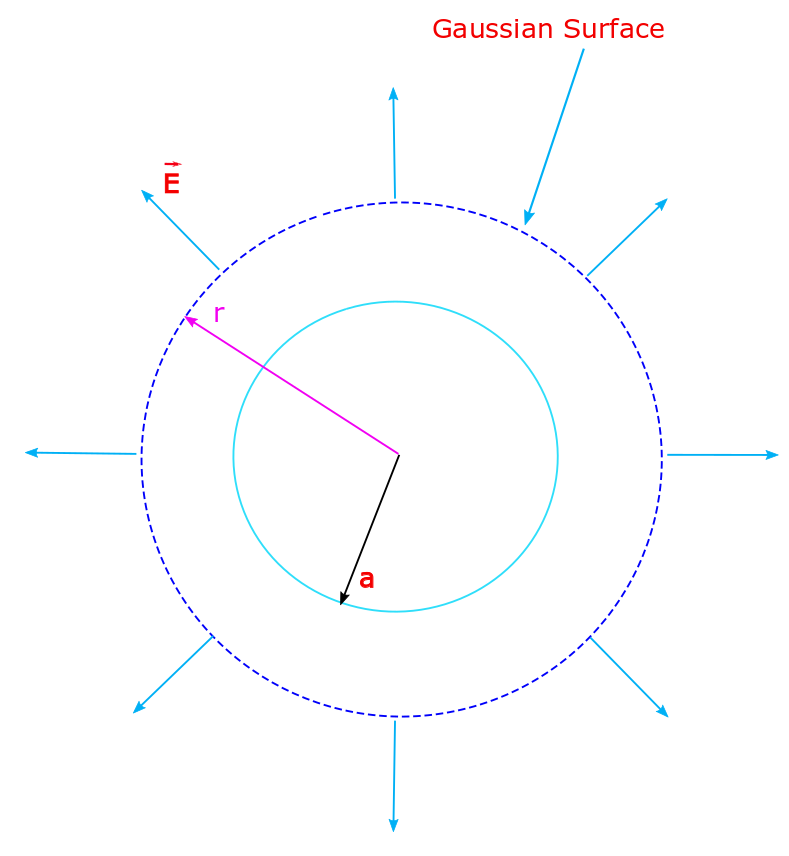
Application of Gauss Law – Cylindrical and Planar Symmetry, Lecture-2
An infinitely long rod of negligible radius has a uniform (linear) charge density of λ. Calculate the electric field at a distance r from the wire. An infinitely long rod possesses cylindrical symmetry. Electric field E must be radially outwards from axis of symmetry of the rod, — for +ve charge. Consider a Gaussian surface…
-
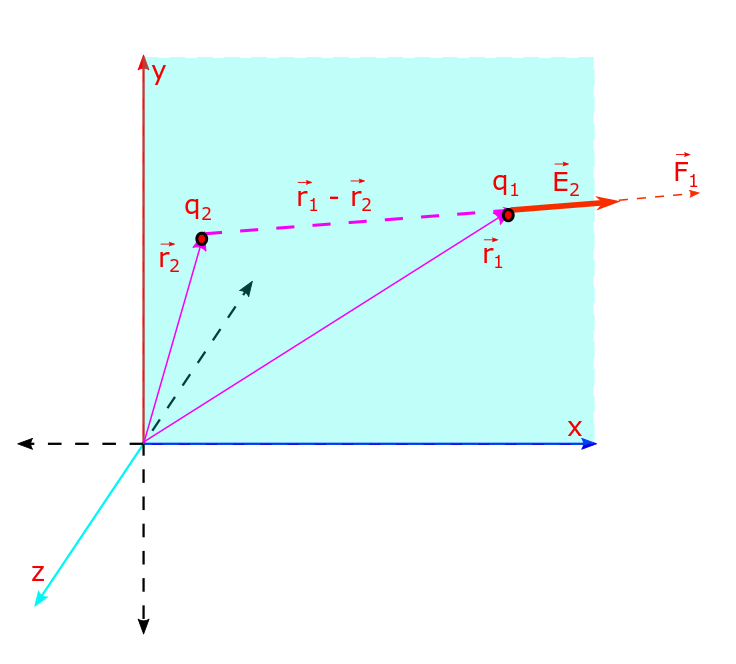
Electric Field and Gauss Law, Lecture 1
Electric field is the amount of Coulomb’s force, that a positive charge of 1 unit experiences at a given position. Its a vector in the same direction as that of the electric force. We will discuss the time independent electric field which is also known as the static field. Advantage over electric force: Coulomb’s force…