Category: Invariance @MDashF
-
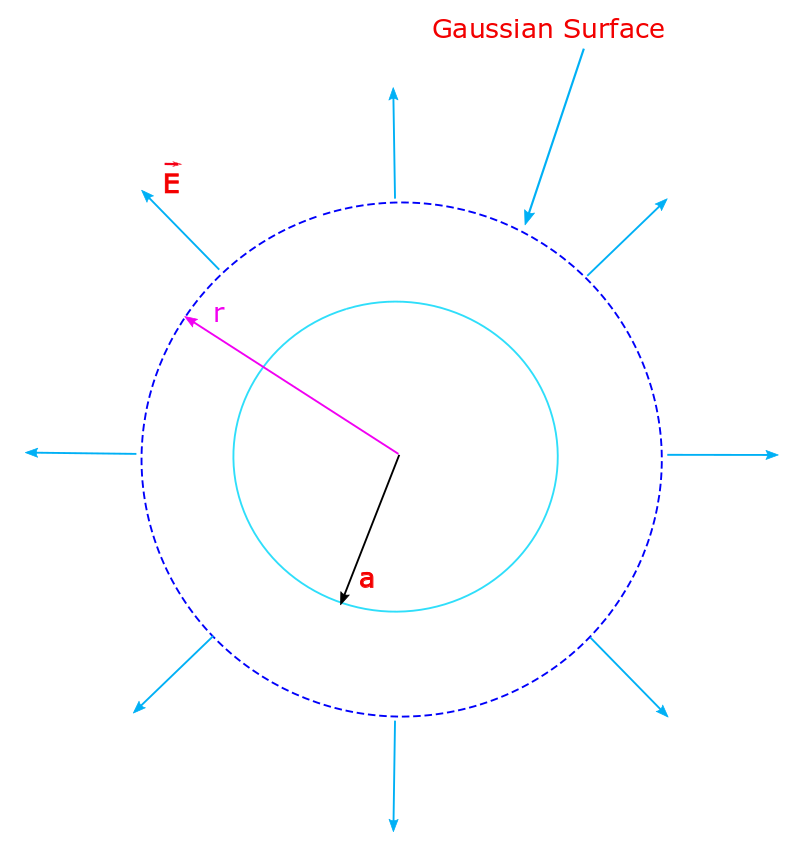
Application of Gauss Law, Spherical Symmetry, Lecture-3
In our last two lectures we laid a good foundation about the concepts of electric field, lines of force, flux and Gauss Law. They can be found here; EML1 and EML2. In the last one we discussed how to apply Gauss Law to find the electric field if cylindrical or planar symmetries are present in…
-
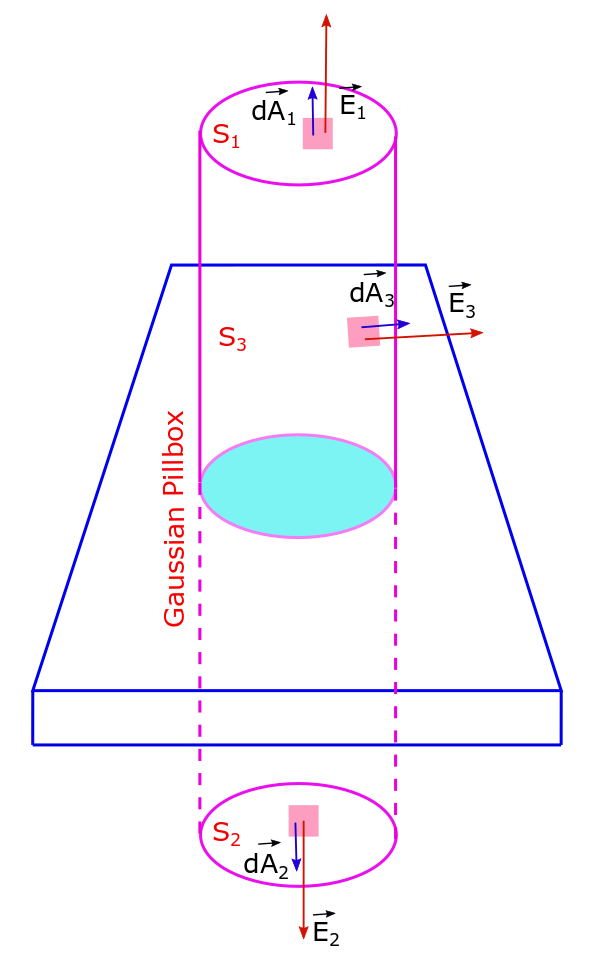
Application of Gauss Law – Cylindrical and Planar Symmetry, Lecture-2
An infinitely long rod of negligible radius has a uniform (linear) charge density of λ. Calculate the electric field at a distance r from the wire. An infinitely long rod possesses cylindrical symmetry. Electric field E must be radially outwards from axis of symmetry of the rod, — for +ve charge. Consider a Gaussian surface…
-
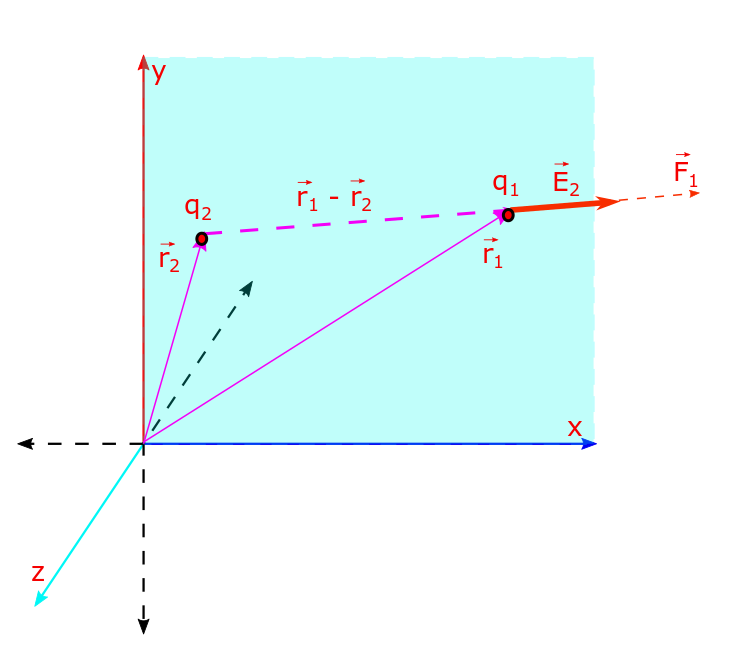
Electric Field and Gauss Law, Lecture 1
Electric field is the amount of Coulomb’s force, that a positive charge of 1 unit experiences at a given position. Its a vector in the same direction as that of the electric force. We will discuss the time independent electric field which is also known as the static field. Advantage over electric force: Coulomb’s force…
-
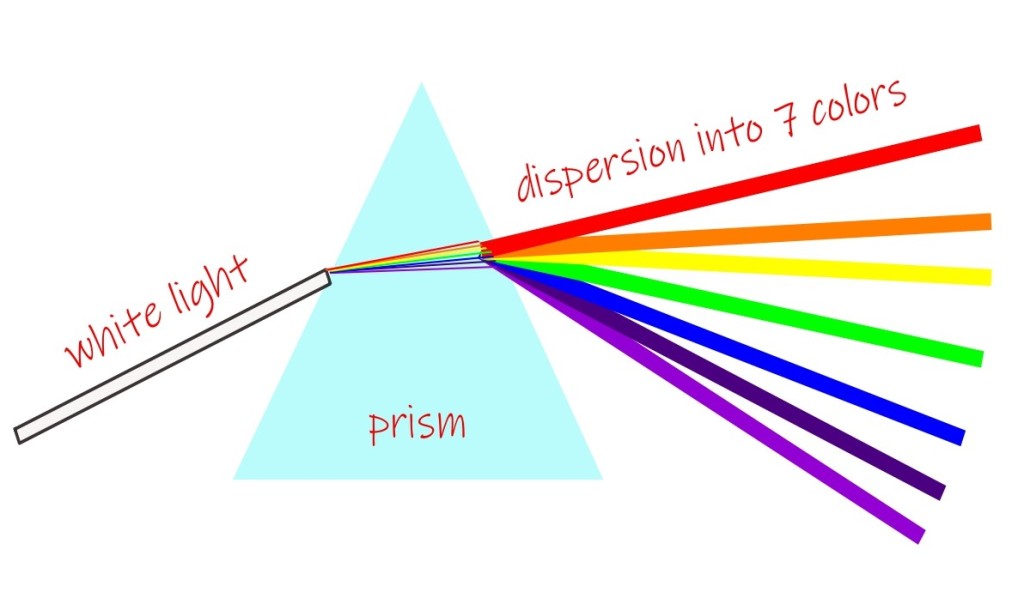
The Bohr model of the Hydrogen atom: atomic spectra and quantization, Quantum Lecture – 4 and 5.
Light is known to have possessed various colors. It would be more appropriate to state that light and color are two entirely distinct entities. Light does not contain color just like you do not contain your spouse. Its another matter you both appear at the same venue on the basis of the same invitation card.…
-

Black body radiation, Quantum Lecture 1.
This article belongs to a group of lectures I intend to prepare for their online dissemination — no hand written notes of the same is available as I did not deliver these lectures, its an attempt at on-the-fly preparation of the concepts, exclusively available at this website. This series is on quantum mechanics and bears…