Category: Invariance @MDashF
-

If you would like to become a nuclear physicist, what you would like to know about the nucleus first?
A. structure of the nucleus Every atom consists of a dense positive central core of mass, known as nucleus. Its size is much smaller compared to the size of the atom, nut nonetheless it contains almost all of the mass of the atom. The nucleus is made of only neutrons and protons. — These are…
-
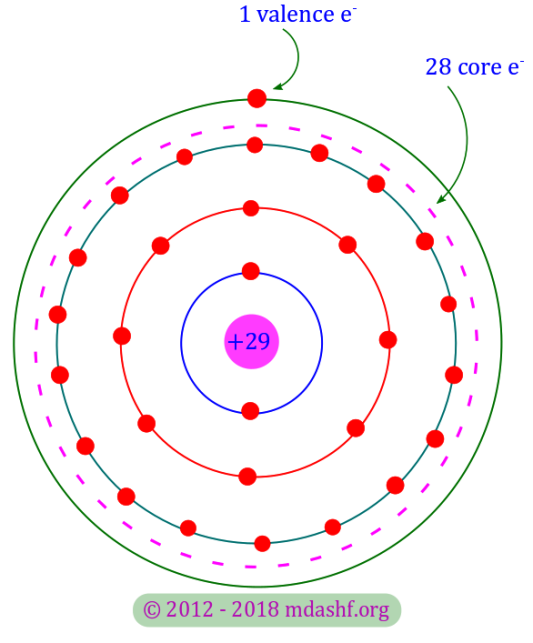
Semiconductors and charge carriers (L-I)
Analog electronics and applications Conductors, semiconductors and holes as charge carriers Topics covered in this lecture A. Conductors B. Semiconductors C. Holes D. Intrinsic semiconductors Conductors: A conductor is the name of a material which is a good conductor of electricity. Copper ( Cu ), Silver ( Ag ) and Gold ( Au ) are…
-

Fundamental types of crystal lattices and their symmetry operations
Fundamental types of crystal lattices and their symmetry operations. Topics covered a. Types and classes of crystals, b. Symmetry operations in crystals In this lecture we will follow through our basic knowledge gained in the last lecture. — lecture — I, II, and shed light on the most interesting properties of crystal lattices, viz. their symmetry…
-

Helmholtz theorem in electrodynamics, Gauge transformation.
Electromagnetic theory, lecture — IV Topics covered in this lecture a. Helmholtz theorem — in electrodynamics b. Gauge transformation — of scalar and vector potential in electrodynamics c. Coulomb and Lorentz gauge All electromagnetic theory lectures of this series, will be found here (https://mdashf.org/category/electromagnetic-theory/) In our previous lecture — lecture — III, we discussed in quite detail,…
-

Helmholtz theorem. Scalar and vector potentials
This lecture develops the formalism of electrodynamics in a very methodical way. It covers the following topics in detail. A. Formalism of electrodynamics — fundamental theorem B. Application of Helmholtz theorem — to electrostatics C. Application of Helmholtz theorem — to magnetostatics